|
|
|
|
QisBool
Polygon & Path Functions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
re-order the sequence of vertices in a polygon to be in counter clock-wise direction. |
|
Prototype |
|
void
QisBool_ConvertToCounterClockwise(int* iXY, int iNV); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
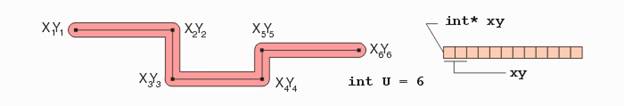
a.
int* iXY: List of x,y co-ordinates for the polygon.
(iNV*2 integers) b.
int iNV: Number of vertices in the polygon. (A
rectangle has 5 vertices). |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* iXY: The newly oriented polygon is written to the
same location as the original polygon. |
|
Return Value |
|
- |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
- |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function re-orders the vertices (iXY) so that
they are in counter-clockwise direction. |
|
Post-Conditions |
|
- |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
static void
IQisBool::ConvertToCounterClockwise(int* iXY, int iNV); |
|
See Also |
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
get the area of a polygon. |
|
Prototype |
|
double
QisBool_GetPolygonArea(int* iXY, int iNV, void* iBooleanHandle); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int* iXY: List of x,y co-ordinates for the polygon.
(iNV*2 integers) b.
int iNV: Number of vertices in the polygon. (A
rectangle has 5 vertices). c.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
- |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
double: Area of the polygon in question. This area is
unit less (number of grids) |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
- |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function computes the area of a polygon in terms
of the number of grids. Since all QisBool co-ordinates are unit less (integer
values), this area unit less too. |
|
Post-Conditions |
|
- |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual
double IQisBool::GetPolygonArea(int* iXY, int iNV) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
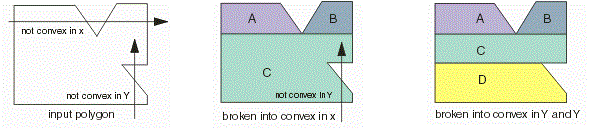
Objective |
|
To
convert a polygon into one or more convex polygons. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_PolyConvexing( int* iXY, int iNV, int*** oXY, int** oNV,
int* oN, EConvexOutput iMode, int iValidateInput,
void* iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int* iXY: List of x,y co-ordinates for the polygon.
(iNV*2 integers) b.
int iNV: Number of vertices in the polygon. (A
rectangle has 5 vertices). c.
EConvexOutput iMode: eNO_CONVEX
: There is no guarantee that the output polygons will be convex (default). eCONVEX_IN_X
: The output polygons are guaranteed to be convex in X. eFULLY_CONVEX
: The output polygons are guaranteed to be convex in X and Y. eTRAPEZOIDS
: The output polygons are guaranteed to be trapezoids. d.
int iValidateInput: 1 (Perform validation of input) or
0 (Assume input is validated) e.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
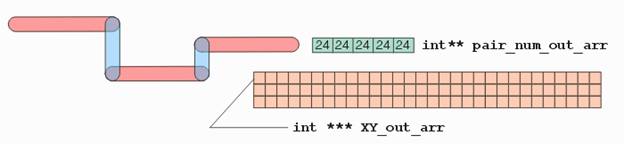
a.
int*** oXY: Address of a double integer pointer which
will point to a newly allocated list of x,y co-ordinates for the output
convex polygons. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer which will
point to a newly allocated list of vertex numbers for the output convex
polygons. c.
int oN: Number of convex polygons generated. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
- |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function converts a polygon into one or more set
of convex polygons depending on the iMode setting. b.
If the polygon is already convex as per iMode, the
output will have the same data as the input. |
|
|
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated by this function to store the
output polygons must be release by calling QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int
IQisBool::PolyConvexing( int* iXY, int iNV, int*** oXY, int** oNV,
int* oN, EConvexOutput iMode, bool iValidateInput ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
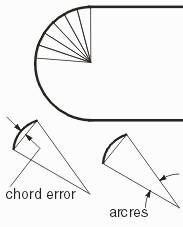
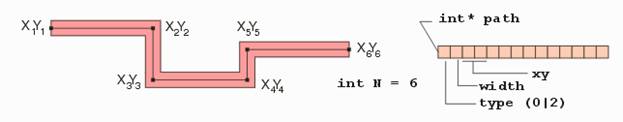
To
convert round paths to boundaries. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_RoundPathToBoundaries( int* iXY, int iNV, int iWidth, int*** oXY,
int** oNV, int* oN, short iArcRes, double iArcSag, void*
iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int* iXY: A list of x,y co-ordinates of the path to be
converted. b.
int iNV: Number of vertices in the path. c.
int iWidth: Width of the path. d.
short iArcRes: The acceptable arc resolution of round
corner of the output boundary. e.
double iArcSag: The acceptable chord error of the
round corner of the output boundary. f.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
|
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int*** oXY: Address of a double integer pointer which
will point to a newly allocated list of x,y co-ordinates for the output
boundaries. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer which will
point to a newly allocated list of vertex numbers for the output boundaries. c.
int oN: Number of output boundaries generated. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
If both iArcRes and iArcSag are both specified, the
parameter with a finer resolution is user. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function converts a round path to a set of
boundaries, one boundary per segment of the path. |
|
|
|
|
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated by this function to store the
output polygons must be release by calling QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int
IQisBool::RoundPathToBoundaries( int* iXY, int iNV, int iWidth, int*** oXY,
int** oNV, int* oN, short iArcRes, double iArcSag ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
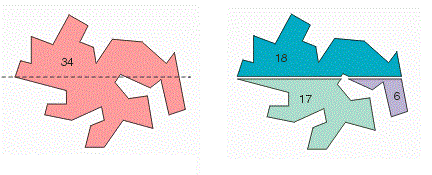
To
group connected boundaries into sets. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_GroupConnectedPolygons( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int*** oXY,
int** oNV, int* oN, void* iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int** iXY: A list of x,y co-ordinates of the
boundaries to be grouped. b.
int* iNV: A list of number of vertices for each of
those boundaries. c.
int iN: Number of input boundaries. d.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int*** oXY: Address of an integer double pointer that
will point to a newly allocated list of index numbers (0 to iN-1) per set of
connected polygons. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer that will
point to a newly allocated list of number of indices per set of connected
polygons. c.
int oN: Number of sets of connected polygons. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
- |
|
Operation |
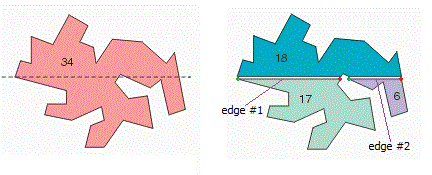
|
a.
This function analyses all of the input polygons (iN,
iNV, iXY) and groups them into oN sets based on connectivity. Any two
polygons from the input set that are geometrically connected fall into the
same set. b.
Each set is represented by a list of indices
corresponding to the polygons belonging to that set. An index to a polygon in
the input set is simply an integer from 0 to iN-1 that contains the data
corresponding to that polygon in iNV and iXY. If I is an index to a polygon
in the input set, iNV[I] stores the number of vertices belonging to that
polygon and iXY[I] points to iNV[I]*2 integers representing it's x,y
co-ordinates. |
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated to store the sets must be
released using QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int
IQisBool::GroupConnectedPolygons( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int*** oXY,
int** oNV, int* oN ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
convert a path (flush or half extended) to boundaries. |
|
Prototype |
|
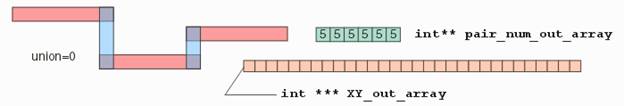
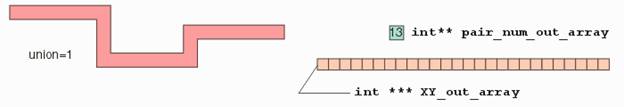
int
QisBool_Path2Boundaries( EPathType iType, int iWidth, int* iXY, int
iNV, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, int iUnionize, void* iBooleanHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int* iXY: A list of x,y co-ordinates of the path to be
converted. b.
int iNV: Number of vertices in the path. c.
int iWidth: Width of the path. d.
int iUnionize: 1 (Unionize the various segments of the
path as one boundary) or 0 (Generate a separate boundary for each segment of
the path). e.
EPathType iType: Type of path eFLUSH_PATH
: flush path eHALFEXT_PATH
: half extended path f.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int*** oXY: Address of a double integer pointer which
will point to a newly allocated list of x,y co-ordinates for the output
boundaries. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer which will
point to a newly allocated list of vertex numbers for the output boundaries. a.
int oN: Number of output boundaries generated. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
Only flush and half extended paths can be converted
using this function. b.
To convert round paths use QisBool_RoundPathToBoundaries. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This function converts a flush/half extended path to
boundaries. b.
If iUnionize is set, the path is converted to one
boundary, otherwise a boundary is generated for each segment of the path. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated by this function to store the
output polygons must be release by calling QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int IQisBool::Path2Boundaries( EPathType iType, int iWidth, int* iXY, int
iNV, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, bool
iUnionize ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
limit the number of vertices in the input polygons by breaking those that
exceed a specified vertex count. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_BreakPolygons( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int iMaxPts, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, int
iValidate, void* iBoolHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int** iXY: A list of x,y co-ordinates of the input
polygons. (iN integer arrays) b.
int* iNV: A list of number of vertices in the input
polygons. (iN integers) c.
int iN: Number of input polygons. d.
int iMaxPts: Maximum number of vertices expected. e.
int iValidate: 1 (Validate input polygons) 0 (Assume
the polygons have been validated) f.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* oN: Address of an integer to store the number of
polygons in the output. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer that will
point to a newly allocated list of number of vertices for each of the output
polygons. (contains oN integers). If I is the index of an output polygon (0
<= I < *oN), then (*oNV)[I] represents the number of vertices for that
polygon. c.
int*** oXY: Address of an integer double pointer that
will point to a new allocated list of x,y co-ordinates for each of the output
polygons. (contains oN integer arrays). If I is the index of an output
polygon (0 <= I < *oN), then (*oXY)[I] is an integer array of (*oNV)[I]
* 2 integers representing the x,y co-ordinates of that polygon. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
If iValidate is 0, it is assumed that the input
polygons are legal and non-re-entrant. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This functions breaks any input polygon which has more
vertices than iMaxPts. |
|
|
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated by QisBool to store the output
polygons (oN, oNV, oXY) must be released using QisBool_Release. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int
IQisBool::BreakPolygons( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int iMaxPts, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, bool
iValidate ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
limit the number of vertices in the input polygons by breaking those that exceed
a specified vertex count and get the edges used to break the polygons. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_BreakPolygonGetEdges( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int iMaxPts, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, bool
iValidate, int** oEdgeArr, int* oNEdges, void*
iBoolHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int** iXY: A list of x,y co-ordinates of the input
polygons. (iN integer arrays) b.
int* iNV: A list of number of vertices in the input
polygons. (iN integers) c.
int iN: Number of input polygons. d.
int iMaxPts: Maximum number of vertices expected. e.
int iValidate: 1 (Validate input polygons) 0 (Assume
the polygons have been validated) f.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* oN: Address of an integer to store the number of
polygons in the output. b.
int** oNV: Address of an integer pointer that will
point to a newly allocated list of number of vertices for each of the output
polygons. (contains oN integers). If I is the index of an output polygon (0
<= I < *oN), then (*oNV)[I] represents the number of vertices for that
polygon. c.
int*** oXY: Address of an integer double pointer that
will point to a new allocated list of x,y co-ordinates for each of the output
polygons. (contains oN integer arrays). If I is the index of an output
polygon (0 <= I < *oN), then (*oXY)[I] is an integer array of (*oNV)[I]
* 2 integers representing the x,y co-ordinates of that polygon. d.
int* oNEdges: Address of an integer to store the
number of edges. e.
int** oEdgeArr: Address of an integer pointer that
will point to a newly allocated list of edges. This list will contain
(*oNEdges) * 4 integers. (*oEdgeArr)[0,1] represents the x,y co-ordinates of
the start point of the first edge. (*oEdgeArr)[2,3] represents the x,y
co-ordinates of the end point of the first edge and so on. |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
If iValidate is 0, it is assumed that the input
polygons are legal and non-re-entrant. |
|
Operation |
|
a.
This functions breaks any input polygon which has more
vertices than iMaxPts and returns a list of edges introduced to break the
polygons. |
|
|
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated by QisBool to store the output
polygons (oNV, oXY) must be released using QisBool_Release. b.
The memory allocated by QisBool to store the edges
(oEdgeArr) must be released using QisBool_ReleaseArray. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
int
IQisBool::BreakPolygonGetEdges( int** iXY, int* iNV, int iN, int iMaxPts, int*** oXY, int** oNV, int* oN, bool
iValidate, int** oEdgeArr, int* oNEdges ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
Objective |
|
To
size a polygon using standard sizing. |
|
Prototype |
|
int
QisBool_PolyCompensation( int* iXY, int iNV, double iSizing, int**
oXY , int* oNV, void* iBoolHandle ); |
|
Input Arguments |
|
a.
int iNV: Number of vertices in the input polygon. b.
int* iXY: x,y co-ordinates of the input polygon (iNV *
2 integers) c.
double iSizing: Amount of sizing to be applied in both
X and Y. d.
void* iBooleanHandle: Handle to an instance of QisBool
obtained using QisBool_Create. |
|
Output Arguments |
|
a.
int* oNV: Address of an integer to store the number of
vertices in the output polygons. b.
int** oXY: Address of an integer pointer that will
point to a newly allocated array representing the x,y co-ordinates of the
output polygon. ( (*oNV) * 2 integers ) |
|
Return Value |
|
a.
success: 0 b.
failure: < 0. Call QisBool_ErrorMsg to get details. |
|
Pre-Conditions |
|
a.
This function uses a very basic form of sizing.
Therefore it must be used only with very simple non-reentrant manhattan data. b.
The output is not guaranteed to be a legal polygon if
the input is not simple. |
|
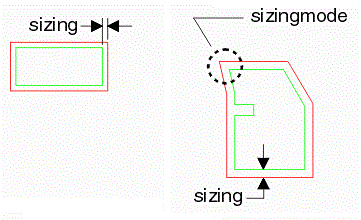
Operation |
|
a.
This function sizes the input polygon by iSizing
amount in X and Y using a very basic sizing technique. |
|
|
|
Post-Conditions |
|
a.
The memory allocated to store the x,y co-ordinates of
the output polygon (oXY) must be released using QisBool_ReleaseArray. |
|
C++ Equivalent |
|
virtual int
IQisBool::PolyCompensation( int* iXY, int iNV, double iSizing, int**
oXY , int* oNV ) = 0; |
|
See Also |
|
|
|
|
|
|
© 2012 Artwork Conversion
Software Inc. |
|
|
417 Ingalls St. Santa Cruz CA
95060 |
|
|
[T] +1 831-426-6163 [F] +1
831-[E] info@artwork.com |
|